What is my gateway address?
Choosing a gateway address on Linux machines is an easy task to perform. Let’s consider a network consisting of three Linux machines as Figure 1 shows.
Let’s consider following subnet and IP addresses:
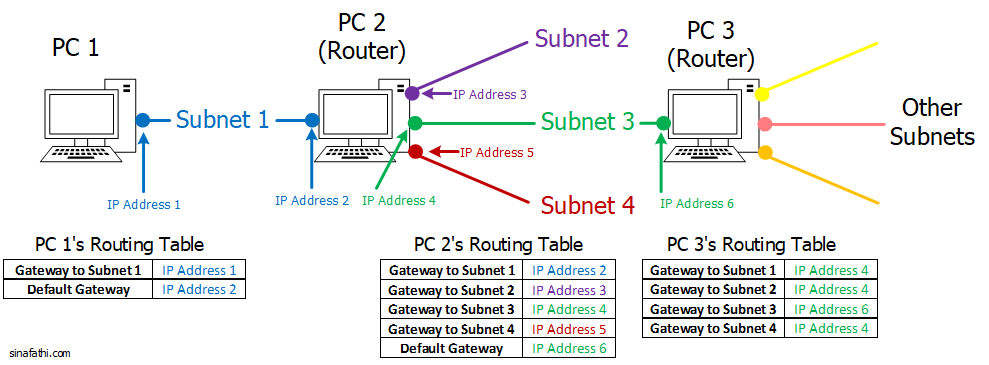
- Subnet 1: 10.0.0.0/24, IP Address 1: 10.0.0.1, and IP address 2: 10.0.0.2.
- Subnet 2: 11.0.0.0/24 and IP Address 3: 11.0.0.1.
- Subnet 3: 12.0.0.0/24 , IP Address 4: 12.0.0.1, and IP address 6: 12.0.0.2.
- Subnet 4: 13.0.0.0/24 and IP Address 4: 13.0.0.1.
Run “route -n” command to check the current routes on each PC. Then use “ip route flush table main” command to clear the routing tables. Also, we need to enable IP forwarding on the routers.
Since PC 1 is only connected to subnet 1, we first add a route to subnet 1 using following command:
$ route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 10.0.0.1
To connect PC 1 to other subnets on the network, we either need to add other subnets addresses to the routing table one by one or add a default gateway to send all the packets not intended for Subnet 1 to that gateway.
$ route add default gw 10.0.0.2
Similar to PC 1, we can add the routes to other PCs on the network based on the tables in Figure 1.
On PC 2:
$ route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 10.0.0.2
$ route add -net 11.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 11.0.0.1
$ route add -net 12.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 12.0.0.1
$ route add -net 13.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 13.0.0.1
And the default gateway is for all the packets to other networks which are not directly connected to PC 2:
$ route add default gw 12.0.0.2
PC 3 is directly connected to Subnet 3, but it is not directly connected to Subnets 1, 2, and 4. To add the routes, we use the following commands:
$ route add -net 12.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 12.0.0.2
$ route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 12.0.0.1
$ route add -net 11.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 12.0.0.1
$ route add -net 13.0.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 12.0.0.1
